Newton Harrison has died, aged 89. With partner Helen Mayer Harrison, Newton was one half of the Harrison Studio. Helen herself died back in 2018. The loss of both Harrisons is a sad moment for eco-artists everywhere. Since the early 1970s when they began co-authoring projects, they were leaders in this field. Ever restless, ever engaged, ever inventing, ever provoking, ever joyful, ever mischievous.
I got to meet Newton twice. Once in 2015, on a family trip to California, I visited him at his home in Santa Cruz and he cooked me a delicious healthy lunch. Helen was still alive at the time, and I met her briefly, but the dementia she experienced in her later years meant she didn’t join us for that meal. The second time I visited their home was in 2018, this time with my collaborator Kim Williams, about a month after Helen had died. Newton welcomed our visit – he said it cheered him up to have us to talk to. We brought gluten free pastries, and sat on the couch drinking tea.
By then Kim and I were in the thick of our project Sugar vs the Reef? which focused on the sugarcane industry of central-northern Queensland and its effects on the Great Barrier Reef. Newton’s interest was piqued as we shared the challenges we were having: working on a project that size; working away from home; trying to bring together multiple stakeholders; and being two small artists up against a massive environmental problem.
One of Newton’s gifts was that he didn’t get bogged down by such minutiae. For us, the 2000km of sugarcane farms and gigantic scale of the adjacent Great Barrier Reef boggled our minds (it was the largest scale we’d ever worked at). But Newton immediately leaped to planetary thinking. What if all the coral reefs of the world were linked through the work? What if they were all mapped and audited and shown to be in peril everywhere?… What if…? (Newton loved talking in “what ifs”). Following this visit with Newton, Kim wrote a blog post about scale and Californian eco-art, including reflections on this encounter.
Of course, we didn’t just go home and carry out Newton’s prescription for the project. We had our own momentum, our own way of working, which was focused on small-scale community interactions in a particular town within the immensity. We worked on a microcosm of the bigger picture. But Newton’s words resonated. During this visit, we were privileged to witness live the Harrisons’ method: when presented with a situation, and when invited to weigh in, he and Helen would actively shift the problem UP in scale, asking the crucial question: How big is here?.
And so while Kim and I worried about the sugar/reef nexus being too big for us, and so far away from our homes, Newton challenged us to reframe our scale of reference, making it even bigger. When we use the word “here”, he asked, where does “here” stop, and where does “there” start? What are the boundaries to “here”? Faced with the onslaught of global heating (which the Harrisons call The Force Majeure – the force that over-rides all other forces), categories like here and there, local and global are all thrown into doubt.
As their career progressed, the Harrisons’ answer to the question how big is here? grew progressively wider until it encompassed oceans, continents, hemispheres, the whole planet and its surrounding atmosphere. It takes a particular kind of imagination to think and talk and make at this scale effectively, to be able to stand and hold the space with governments and corporations and scientists, and the Harrisons had that.
At the end of that 2018 visit, Newton took us over to the Santa Cruz Botanic Gardens, where we got to see the Future Gardens project. Here’s a link to a brief blog post I wrote at the time about that project. This project investigates the survival of native Californian plant species under three possible future heat and rainfall scenarios. It was just about to launch, and the Harrisons had secured a contract with the Botanic Gardens to maintain it for at least 50 years. Once again, our thoughts turned back to scale. How long is now? What if a project needs to run for multiple generations?
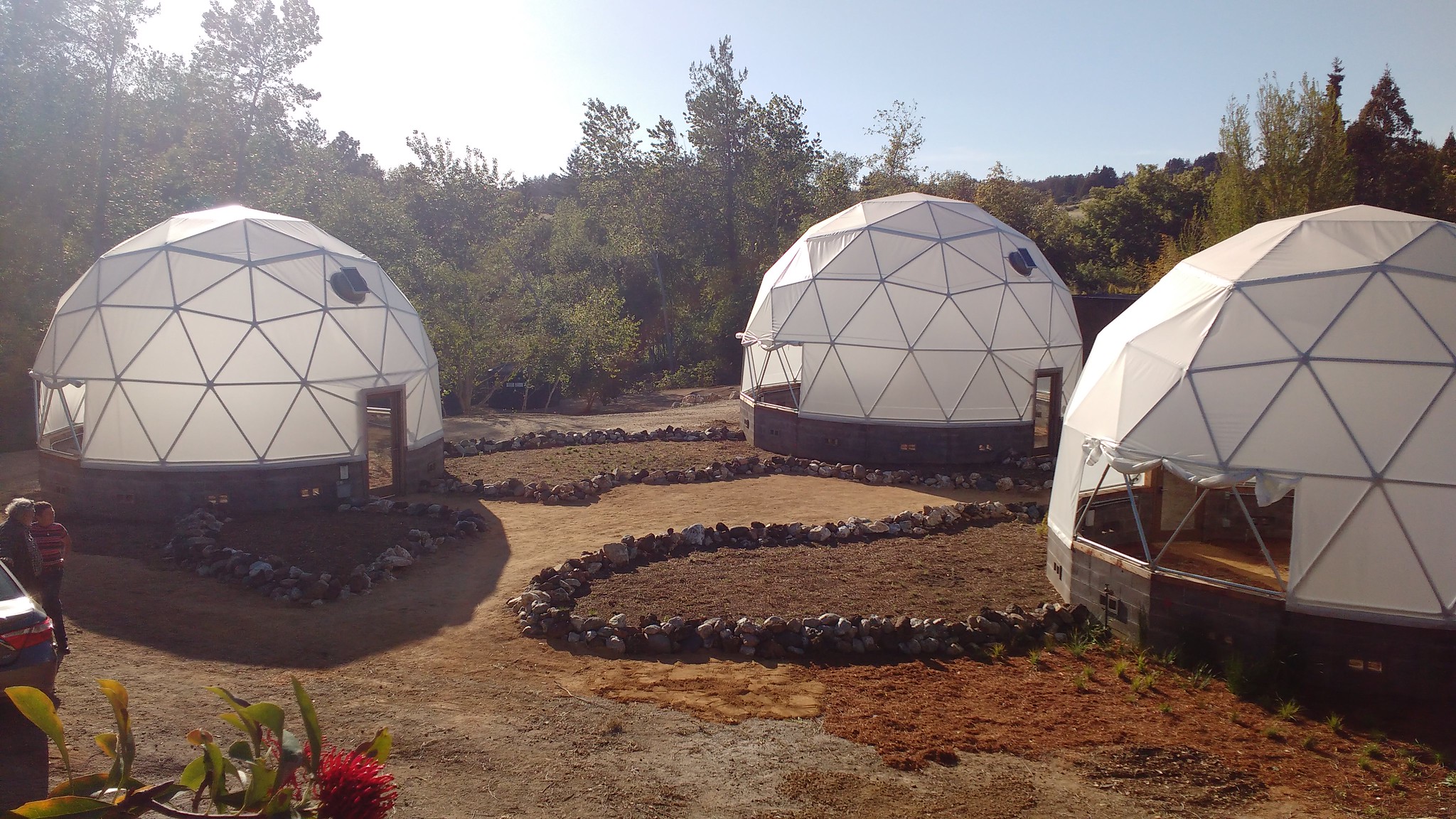

Here’s a short video produced by University of California Santa Cruz about the Future Gardens project.
For me, as an artist half their age, the Harrisons’ legacy is continually useful. One of the reasons for this is that they took seriously the work of describing, interpreting, and communicating about their own experiences. They left behind an enormous archive of correspondence, project proposals, critical reflections, and documentation (now housed at Stanford University). Kim and I spent a few days immersed in this around the same time we visited Newton. In that archive, you can dive into a particular project to see how they made it happen. Kim, I remember, spent a long time rummaging around in the Sava River project. Faxes, emails, thousands of phone calls, haggling for invoices to be paid, photographs from site visits, fragments of poems, endless negotiation, manila folders, it’s all in there. It’s striking how seldom a project “progressed smoothly”. The Harrisons had an appetite for difficulty.
Collaborating with councils, governments, scientists and communities takes a lot of admin, which is not just “behind the scenes” stuff: it IS the work. Projects can take years, and they can go nowhere. They can sit dormant for decades and then bubble up and accelerate again. All these records of project management in the archives are material for future art historians to study, if only they could recognise this as central to the work of contemporary art. Bubbling around and through all of this is the spirit of the Harrisons: the inventive leaps of imagination, the metaphors and lateral re-framings of a situation, the judo moves that turn an intractably stuck problem into something thrilling, and with great potential for change. Chris Fremantle’s essay “Making Poetry to Invent Policy” offers some reflections on this.
(NB – Connected to this, and very much in the tradition of the Harrison Studio, is the work of Metabolic Studio in Los Angeles – their Bending the River project is in it for the long haul!)
Helen and Newton were a married couple who collaborated for at least fifty years. Kim and I are friends and colleagues rather than a couple, but something that I learned from the Harrisons was that you can be an artist duo or group and still maintain distinct voices. Their Lagoon Cycle (and many other works) incorporated dialogues which dramatised the social and environmental problems that were an integral part of the project. They did not smooth these problems over with a unified voice which swept disagreement and glitches under the carpet. You can hear them bickering in some of these dialogues (in a thoughtful, poetic way).
Following the Harrisons, at times Kim and I have played around with a similar dialogical format for thinking through the unresolvable dilemmas that characterise socially-engaged art with an environmental focus. It’s liberating to remind ourselves that we don’t always have to agree. In fact, the disagreement can be the thing.
Below is a work we made for the 2020 Biennale of Sydney, entitled The Growing Up Hub“. Click on the image to see it larger and read the dialogue. You can read a reflection on this piece and its connection to the Harrisons here.
More on the dialogical nature of this kind of art: I remember that we were intrigued when Newton told us about his and Helen’s method of scheduling “Daily Conversations” as an important part of their working process. Kim and I trialled something similar, particularly during intense periods of working on Sugar vs the Reef?. Anxieties: would the crops grow, and would they grow in time, and would a cyclone wipe out the whole project, and would our collaborators quit on us, and would our hosts continue to support us? Adapting the Harrisons’ daily conversational ritual helped us to stay a little more level-headed during stressful times, to face the anxieties that are integral to complex socially engaged artworks, rather than simply wishing them gone.
I want to finish with three valuable principles from Newton and Helen. Once again, these are examples of the “reframing” tactics at which they excelled. All three of these principles continue to challenge me in my ongoing work.
1 – Working by invitation.
On page 64 of their Force Majeure book, the Harrisons talk about the moment (in 1976!) when they “invented their fundamental contract”:
We would go to a place only by invitation; we would accept an invitation only if it included some means for networking into a larger community; we would agree only to go for a week or two at first, to think and research. To earn our way we would sing for our supper, so to speak, by speaking or performing. If an idea of consequence to us came forward, we would present it, and if funding and interest arose, we would enact and evolve whatever concept emerged. We took for granted that the work would be eco-political in nature because that is who we were as artists. We also took for granted that simply having the opportunity to make the proposals would not be enough to cause them to be enacted.
2 – Ecosystem as client.
While the “business name” Harrison Studio, and their way of operating, meant that they presented themselves to the world somehow like a design firm, the Harrisons always maintained that their main client was the ecosystem. This relationality with entities that go beyond the human continued right up until Newton’s death. Towards the end, it seemed to me, things had moved beyond a “client” and “service provider” relationship, towards … something more. I was particularly affected by the dialogue he had with the Mediterranean Sea in this beautiful video. And as recently as July, when Newton posted on facebook about his pancreatic cancer, he published a moving dialogue with the lifeweb.
3 – The Ennobling Principle.
The Harrisons sometimes described the scale at which they operated as “worldscapes”. When attempting to interact with worldscapes, they urged, any resolution of a problem must be ennobling of both people and place. There is a fundamental ethics here. Big moves are required to face the Force Majeure; and at the same time, solutions cannot ride roughshod over place and people. Means and ends must align:
Worldscapes are problems with global reach that have three properties: They refer to complex systems for which single cause and effect solutions are ineffectual. The problem itself reveals the disciplines required for resolution as well as determining how deeply the people involved must engage these disciplines. Multiple feedback loops are inherently part of the process. Any resolution both ennobles the place in question and the people at work.
Farewell Newton. You and Helen gave the world so much: we have a rich archive of your stories and documents to build from; we have a strong set of working principles to guide and provoke our ongoing work; and we have your voices of encouragement to keep at it.